Biometric Citizen Database
In a country facing challenges like natural disasters, terrorism, and corruption, a system was needed that could secure citizens’ identities in a transparent and fast way. Pakistan answered this need by creating the world’s largest Biometric Citizen Database, a system that not only transformed how citizens are identified but also reshaped governance itself.
Thanks to this system, everything from SIM card registration to financial aid distribution is now possible with complete transparency. Managed by NADRA (National Database and Registration Authority), this database holds the fingerprints, photographs, and personal details of millions of Pakistanis.
This initiative is considered one of the most significant steps in Pakistan’s history, and international media like The Washington Post has called it “the world’s largest and fastest biometric information collection drive.”
Biometric Citizen Database – Key Details
| Aspect | Information |
| Managing Authority | NADRA (National Database and Registration Authority) |
| Citizens Registered | Over 121 million |
| Stored Data | Ten fingerprints, digital photos, biographic details |
| Main Purpose | Counter-terrorism, transparent governance, aid distribution |
| Global Standing | World’s largest multi-biometric citizen database |
What is the Pakistan Biometric Database and How Does it Work?
The Pakistan Biometric Citizen Database is a digital system that stores every citizen’s fingerprints, photos, and personal information. Managed by NADRA, it is among the most advanced databases in the world.
The biggest advantage is speed and accuracy. Whether it’s buying a SIM card, opening a bank account, or registering for a government welfare program, identity can be verified within seconds.

How Did the Pakistan Biometric Database Help Verify Mobile SIMs?
In 2015, the government of Pakistan made biometric verification mandatory for all mobile SIMs. Using the Pakistan Biometric Database, mobile companies matched users’ fingerprints and CNIC details against NADRA’s records.
- If the data matched, the SIM stayed active.
- If it didn’t, the SIM was blocked.
This step played a major role in fighting terrorism by eliminating fake SIMs that were being used by criminals and terrorists.
How Did the Pakistan Biometric Database Help in Counter-Terrorism?
Terrorists in Pakistan often used unregistered SIMs to plan attacks and blackmail people. With the Pakistan Biometric Database, it became nearly impossible for anyone to buy a SIM card under a fake name.
Law enforcement agencies could now trace every call or text back to its real owner. This strengthened the fight against terrorism and made it harder for criminals to hide behind fake identities.

How Did the Pakistan Biometric Database Ensure Fair Aid Distribution?
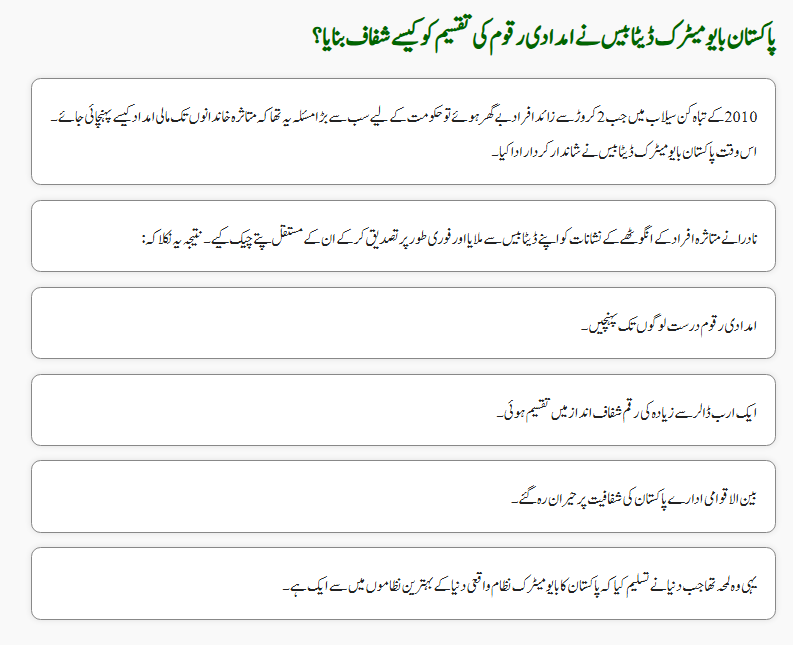
During the devastating floods of 2010, more than 20 million people were displaced. The biggest challenge for the government was: how to distribute financial aid fairly?
The Pakistan Biometric Database provided the solution. NADRA matched victims’ thumbprints with their permanent addresses to confirm who was truly affected.
The results were groundbreaking:
- Aid money reached the right people.
- Over $1 billion was distributed transparently.
- International organizations praised Pakistan’s fairness.
This proved that technology could bring honesty and efficiency even during national emergencies.
How is the Pakistan Biometric Database Helping with Tax Reforms?
Tax evasion is a major problem in Pakistan. But with the help of Pakistan Biometric Database and NADRA’s big data analytics, things are changing.
By linking multiple government databases, NADRA identified around 3.5 million people who were eligible to pay taxes but had never done so. If even a minimum tax was applied to them, Pakistan could instantly collect billions of dollars in revenue.
This database has become a foundation for future tax reforms and a more transparent financial system.
What is the Global Impact of the Pakistan Biometric Database?
The Pakistan Biometric Database has earned international recognition for its size, speed, and transparency.
- Countries like India and South Africa have also adopted biometric systems, but Pakistan’s large-scale and rapid implementation is unmatched.
- Major publications like Washington Post and Forbes have called it a model for other developing nations.
- Most importantly, it has built trust between citizens and the state — something that fragile democracies often struggle with.

Conclusion
Through the Pakistan Biometric Database, Pakistan has not only strengthened its fight against terrorism but also ensured fair aid distribution, improved tax reforms, and built a transparent system of governance. This database continues to make everyday life easier for millions of Pakistanis.
If Pakistan keeps upgrading this system with advanced technology, it can further improve citizen services and gain global recognition as a leader in digital governance.
Related Posts